Sep 30 13:39:34 gnu kernel: audit: type=1130 audit(.485:42): pid=1 uid=0 auid= ses= msg='unit=user-runtime-dir@976 comm='systemd' exe='/us Sep 30 13:39:34 gnu systemd3033: pamunix(systemd-user:account): account sddm has expired (account expired) Sep 30 13:39:34 gnu systemd3033: PAM failed: User account has expired Sep 30 13:39:34 gnu systemd3033: user@976. Mar 16 12:29:56 authpriv.err sshd30694: error: PAM: User account has expired for tuser from 10.109.4.20 Mar 16 12:29:56 authpriv.info sshd30694: Failed keyboard-interactive/pam for tuser from port 60942 ssh2. In a few clicks, you can find any user accounts that expired, so you can determine whether they are still needed or can be deleted as part of IT housekeeping procedures. You can easily filter the results and export the list of expired user accounts to any of multiple file formats, including CSV.
Disabled accounts

If an organization has a provisioning process in place for governing (automatically) the enabling and disabling of account status and (or) there is a good frequency of guest / vendor engagement, this process is very effective. Owing to the uncertainty attached to such vendor engagement that has an uncertain expiry date, an automated process can't be preset.
Also in a scenario where a vendor engagement needs to be controlled due to inactivity, the account can be disabled provisionally for security and can be re-enabled upon need.
A disabled account can be set at: Account -> Properties -> Account tab ->Account Options -> select checkbox 'Account is disabled'
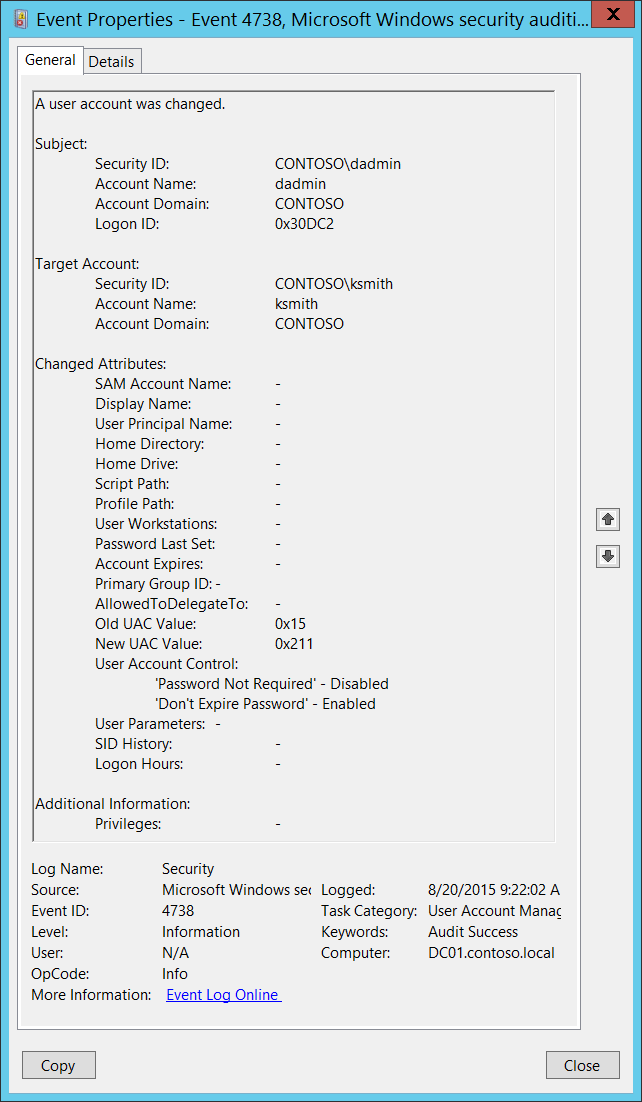
Locked accounts
An account can be locked automatically based on the organization's Account Lockout Policy. Supposing such a process is not in place, the account could be compromised and proves fatal to the organizational data.
One must not trust the event logs wholly too. The logs are generated in large volumes and it is impossible to crack a potential breach from an account that does not conform to the Account Lockout Policy or to manually disable every single account for that matter.
The Account lockout threshold can be set at group policy: Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings ->Security Settings -> Account Policy -> Account Lockout Policy.
Expired accounts

For organizations depending largely on contract-based assignments, this utility is a boon. The privilege of setting an account expiry time saves you the trouble of remembering and having to come back to it manually upon expiry. When the contract comes to an end, the account automatically expires thus providing no scope for security breaches. Also, if an account provisioning process is in place, this setting clearly adapts to suit it.
Expired account can be set at: Account -> Properties -> Account tab -> Account expires -> End of
Key difference after Status change:
All accounts behave similarly after the change except, the only difference being that of the locked accounts. Where, the account remains locked only for a specified duration and can be ‘automatically' unlocked upon completion of the said duration. If duration is set to 0, it will never be ‘automatically' unlocked.
User's Account Has Expired Processmaker
If an organization has a provisioning process in place for governing (automatically) the enabling and disabling of account status and (or) there is a good frequency of guest / vendor engagement, this process is very effective. Owing to the uncertainty attached to such vendor engagement that has an uncertain expiry date, an automated process can't be preset.
Also in a scenario where a vendor engagement needs to be controlled due to inactivity, the account can be disabled provisionally for security and can be re-enabled upon need.
A disabled account can be set at: Account -> Properties -> Account tab ->Account Options -> select checkbox 'Account is disabled'
Locked accounts
An account can be locked automatically based on the organization's Account Lockout Policy. Supposing such a process is not in place, the account could be compromised and proves fatal to the organizational data.
One must not trust the event logs wholly too. The logs are generated in large volumes and it is impossible to crack a potential breach from an account that does not conform to the Account Lockout Policy or to manually disable every single account for that matter.
The Account lockout threshold can be set at group policy: Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings ->Security Settings -> Account Policy -> Account Lockout Policy.
Expired accounts
For organizations depending largely on contract-based assignments, this utility is a boon. The privilege of setting an account expiry time saves you the trouble of remembering and having to come back to it manually upon expiry. When the contract comes to an end, the account automatically expires thus providing no scope for security breaches. Also, if an account provisioning process is in place, this setting clearly adapts to suit it.
Expired account can be set at: Account -> Properties -> Account tab -> Account expires -> End of
Key difference after Status change:
All accounts behave similarly after the change except, the only difference being that of the locked accounts. Where, the account remains locked only for a specified duration and can be ‘automatically' unlocked upon completion of the said duration. If duration is set to 0, it will never be ‘automatically' unlocked.
User's Account Has Expired Processmaker
Event ID in logon event.
2003:
531: Logon failure. A logon attempt was made using a disabled account.
User Account Has Expired Windows 10
532: Logon failure. A logon attempt was made using an expired account.
539: Logon failure. The account was locked out at the time the logon attempt was
made Mail merge word for mac with excel converter not found.
Active Directory User Account Expiration
2008:
Processmaker User's Account Has Expired
The 2008 equivalent of ALL failed logon events is: '4625: An account failed to log on'
Failure reason: Same as above
Comments
User Account Has Expired Spring Security
2017 mac desktop. comments
